Reducing Impacts and Solar-Environmental Synergies
Ecosystem Services of Agrivoltaics
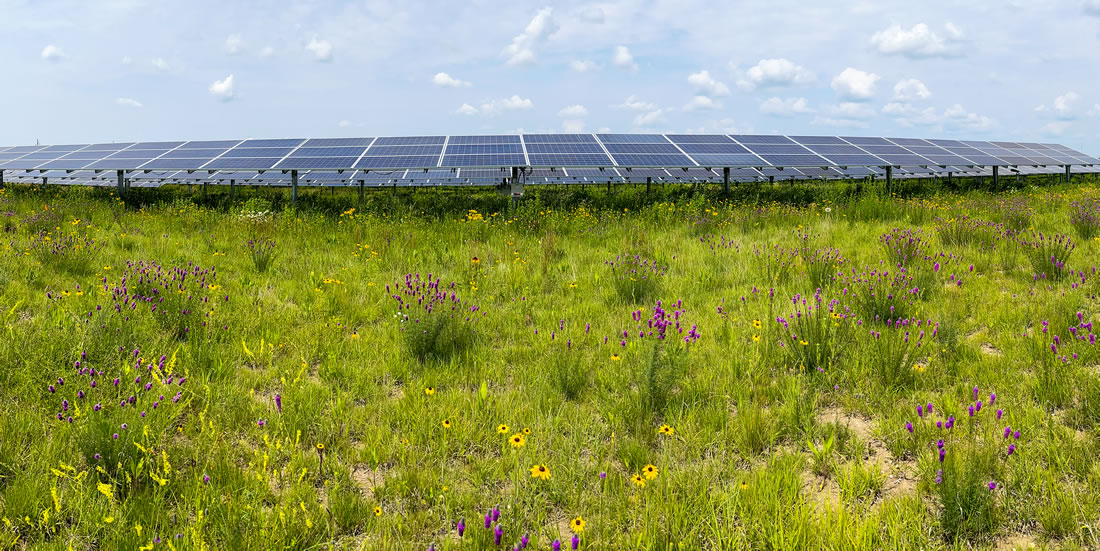
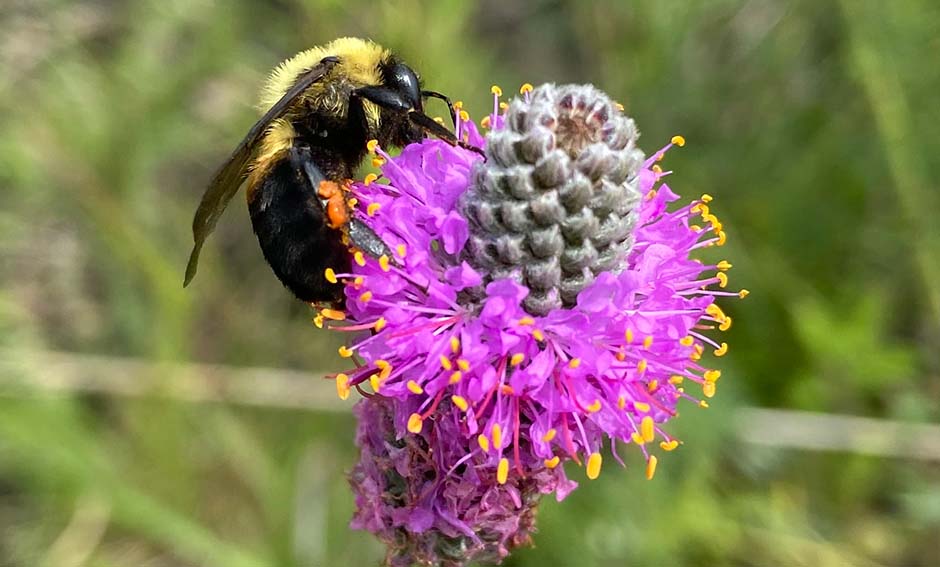
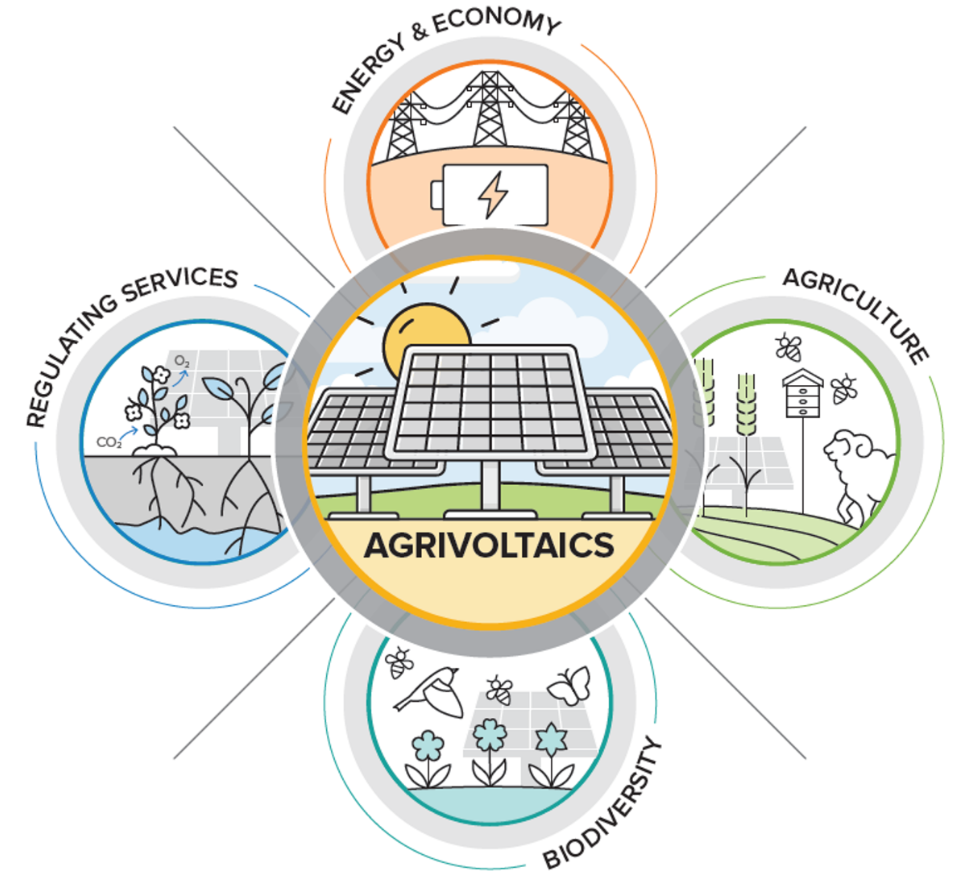
Dual land uses that co-locate solar energy, biodiversity conservation, and agricultural production, often termed “agrivoltaics”, have great potential to mitigate the environmental impacts of solar energy and optimize the optimize the outputs of solar energy production and other ecosystem services such as biodiversity and food production. Through the DOE InSPIRE Project and other projects, Argonne has examined the ecosystem services of native habitat establishment at solar facilities (“solar-pollinator habitat”) as a means to improve the environmental compatibility of large-scale solar developments.
Below are scientific articles and presentations authored or co-authored by Argonne scientists on the potential ecosystem services of solar-pollinator habitat:
- Examining the Potential for Agricultural Benefits from Pollinator Habitat at Solar Facilities in the United States
- Modeling the Ecosystem Services of Native Vegetation Management Practices at Solar Energy Facilities in the Midwestern United States
- Opportunities for agrivoltaic systems to achieve synergistic food-energy-environmental needs and address sustainability goals
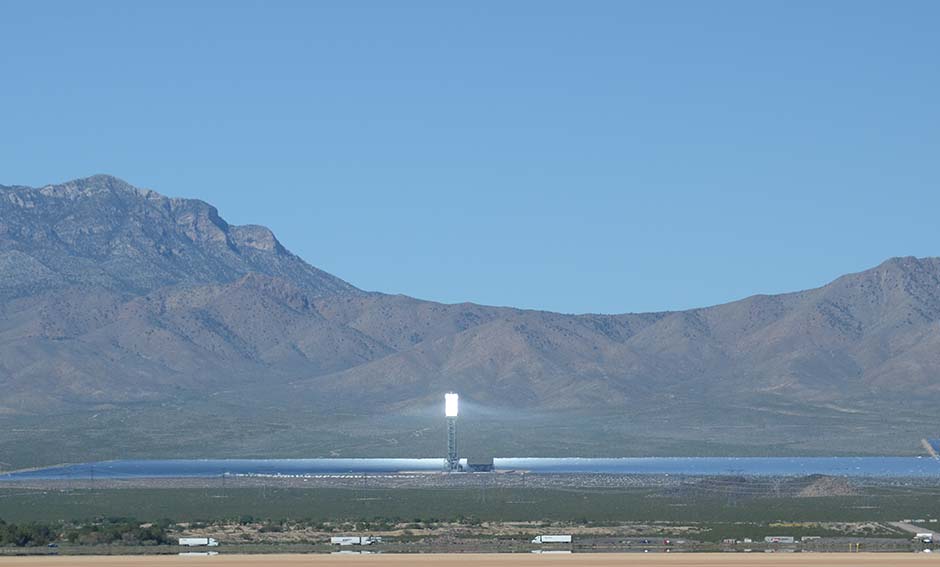
Visual Impact Assessments
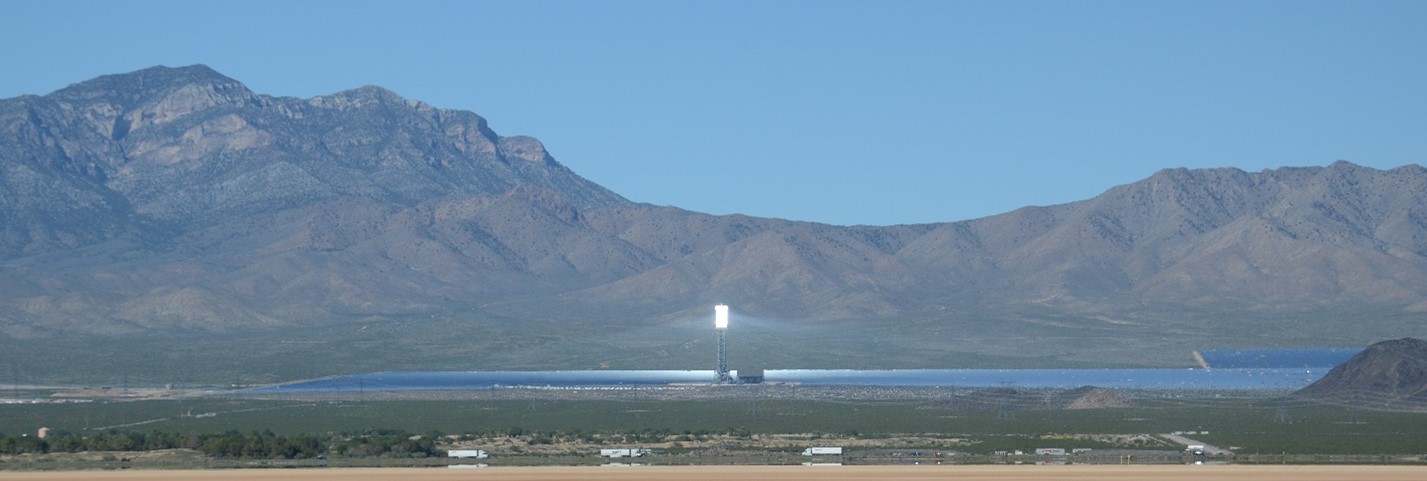

Combining field measurements with computer models, Argonne scientists have conducted innovative visual impact assessments for a variety of solar energy facilities, including quantification of visual contrast, glint, and glare. Featured visual assessment publications include the following:
Soil Health
Argonne scientists have initiated a study to develop a monitoring framework to better understand soil health implications of solar energy facilities. This 3-year solar-soils project funded by the U.S. Department of Energy Solar Energy Technologies Office focuses on:
- Establishing best practices and methods for quantifying soil constituents (including carbon, pesticides, and select nutrients and metals) at ground-mounted solar energy facilities;
- Contributing to a publicly available national database on soil organic carbon (SOC); and
- Investigating SOC cycling and soil-based carbon storage potential for solar facilities.




